The invention of the transistor in the 1940s changed electronics forever. It made devices smaller, more powerful, and efficient. This was thanks to bipolar junction transistors and semiconductor materials. These advancements are key to modern electronic circuits.
Transistors, like NPN and PNP, are vital in the electronics world. They help make complex circuits for many uses. The use of semiconductor materials in transistors has led to smaller, faster, and more efficient devices. This has greatly impacted electronics.
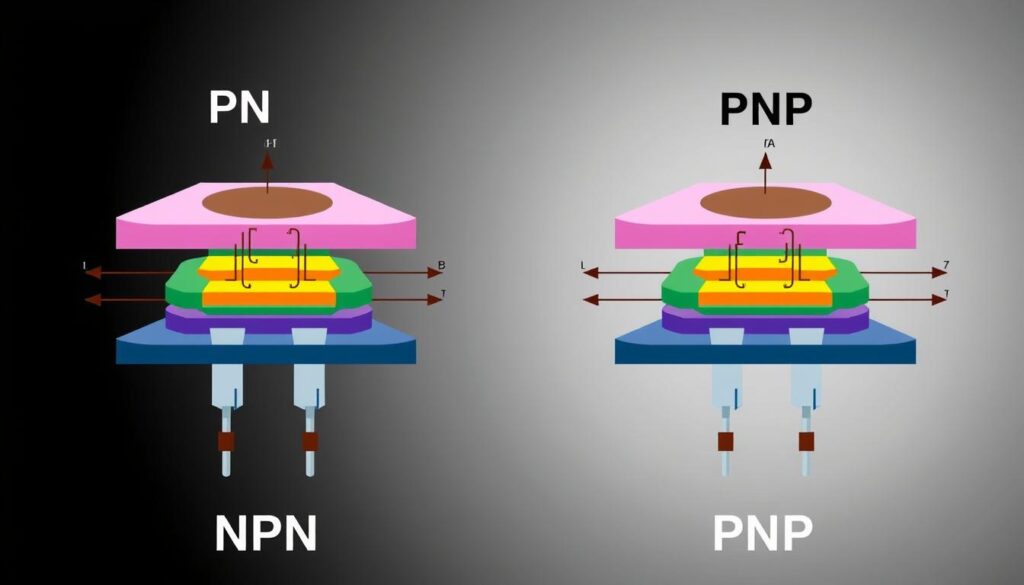
NPN and PNP transistors use n-type and p-type materials. They have three layers, which is basic for electronic circuits. Knowing the difference between NPN and PNP transistors is key for making efficient circuits. This includes those in industrial control systems.
Key Takeaways
- NPN transistors are characterized by current flowing from the collector terminal to the emitter terminal.
- PNP transistors feature current flow from the emitter terminal to the collector terminal.
- NPN and PNP transistors are used in a wide range of electronic circuits, including industrial control systems.
- The output current limitation for proximity sensors typically reaches up to 200 mA.
- NPN transistors are referred to as “sinking outputs”, while PNP transistors are referred to as “sourcing outputs” in electronic circuits.
- Understanding the differences between NPN and PNP transistors is essential for designing and building efficient electronic circuits.
Introduction to Transistor Technology
Transistors are key in today’s electronic devices. They’ve changed the semiconductor world. Thanks to transistors, devices are now smaller, faster, and more efficient. This is because transistors use special materials that can both conduct and insulate electricity.
The first Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) were made in 1947. Ever after, transistor tech has kept getting better. Now, transistors power everything from phones to computers.
What is a Transistor?
A transistor is made of three layers of silicon. These layers are set up in a special way, either NPN or PNP. This setup controls how current flows. Transistors can amplify signals or act as switches, making them perfect for many uses.
Historical Development of Transistors
Transistor development has seen big leaps in materials and design. New materials like silicon have boosted their performance. Also, better manufacturing methods have made transistors cheaper and more common.
Impact on Modern Electronics
Transistors have changed electronics a lot. They’ve made devices smaller, faster, and more efficient. The semiconductor industry has grown a lot because of transistors. They’re used in many things, from gadgets to industrial tools. As transistor tech keeps improving, we can expect even more amazing devices.
Basic Principles of Semiconductor Operation
Semiconductors work by moving charge carriers like electrons and holes. A small input current or voltage controls this movement. This allows for devices that can boost or switch electronic signals.
The material’s conductivity is key to how semiconductors work. By adjusting conductivity, they can make many devices, from simple switches to complex amplifiers. Insulators, with their low conductivity, help keep devices separate and prevent interference.
Some important traits of semiconductor materials are:
- High conductivity
- Low power use
- Fast switching speeds
These traits make semiconductors perfect for many electronic devices. This includes computers, smartphones, TVs, and radios.

In summary, semiconductors operate by controlling charge carrier movement and conductivity. Understanding these basics helps us make devices that can enhance or change electronic signals. These devices are found in many electronic products.
| Semiconductor Material | Conductivity | Insulators |
|---|---|---|
| Silicon | High | Low |
| Germanium | Medium | Low |
Understanding NPN and PNP Transistors
NPN and PNP transistors are key parts in electronic devices. NPN transistors have two n-type materials with a p-type layer in between. PNP transistors have two p-type materials with an n-type layer in between.
NPN transistors are used in most digital circuits, like microprocessors and logic gates, about 70% of the time. PNP transistors are used about 30% of the time, mainly where a negative ground is needed.
NPN Transistor Structure
NPN transistors can amplify signals efficiently, thanks to their current gain (beta) of 100 to 1000. They are fast and can handle a lot of current.
PNP Transistor Structure
PNP transistors also have a current gain (beta) of 100 to 1000, making them good for amplification. They can handle high voltages and offer better isolation between input and output.
Key Differences Between NPN and PNP
The main differences are in structure, application, and usage. Knowing these differences helps choose the right transistor for a project.
| Transistor Type | Current Gain (beta) | Switching Speed |
|---|---|---|
| NPN | 100-1000 | Up to 100 MHz |
| PNP | 100-1000 | 20-50 MHz |
In conclusion, NPN and PNP transistors are vital in electronics, each with unique features and uses. Understanding their structures and differences helps in making the right choice for projects.
How Transistors Function as Switches
Transistors work in three modes: active, cutoff, and saturation. In the active mode, they can boost signals, making them key in electronic circuits. As transistor switches, they manage current flow, letting it pass or block as needed. This is vital in amplifiers and digital logic circuits.
In cutoff mode, the transistor is off, and no current flows. This is good for making digital logic gates, like AND and OR gates. The saturation mode, on the other hand, lets maximum current flow, perfect for high current needs.

When using transistors as switches, consider the base current, collector current, and base-emitter voltage. For instance, an NPN transistor needs a certain voltage (VIN > 0.7 V) to turn on. A PNP transistor needs a base voltage more negative than the emitter. Knowing these details is key for making electronic circuits that use transistor switches and amplifierswell.
Here are some key points to consider when working with transistors as switches:
- Base current and collector current are critical parameters to consider
- Voltage applied between the base and emitter determines the switching mode
- Saturation mode allows maximum current flow, while cutoff mode blocks current flow
- Understanding transistor parameters is essential for designing efficient electronic circuits
Biasing Techniques for Transistor Circuits
Transistors are key in electronic devices. They work by moving charge carriers. Biasing techniques help control this movement.
These techniques apply a small current or voltage. This lets the transistor act as an amplifier or switch.
Biasing is vital for transistor circuits. It sets the transistor’s operating point. This point is shown by collector current (IC) and collector-emitter voltage (VCE) without a signal.
There are many biasing techniques. These include forward bias, reverse bias, and active region operation.
Forward Bias Configuration
In forward bias, the base-emitter junction is forward-biased. The base-collector junction is reverse-biased. This setup is common for transistor circuits.
It lets the transistor work in the active region.
Reverse Bias Configuration
In reverse bias, the base-emitter junction is reverse-biased. The base-collector junction is forward-biased. This setup is less common but used in some circuits.
Active Region Operation
In the active region, the transistor amplifies signals. The collector current is directly related to the base current. This is the most common operating state for transistors.
The table below shows the main biasing techniques for transistor circuits:
| Biasing Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Forward Bias | Base-emitter junction is forward-biased, and base-collector junction is reverse-biased |
| Reverse Bias | Base-emitter junction is reverse-biased, and base-collector junction is forward-biased |
| Active Region Operation | Transistor operates as an amplifier, and collector current is proportional to base current |
Biasing techniques are critical for transistor circuits. They set the transistor’s operating point. Knowing these techniques helps designers make efficient electronic devices.
Common Applications in Electronic Circuits
Transistors are key in many electronic circuits, like amplifiers, switches, and oscillators. They can boost or switch electronic signals. This makes them essential in today’s gadgets. In electronic circuits, they act as amplifiers to strengthen signals or as switches to manage current flow.
Transistors are found in audio amplifiers, radio transmitters, and computer circuits. They help these devices work right by amplifying or switching signals. For instance, in an audio amplifier, a transistor boosts a weak audio signal so it can be heard through a speaker.

Transistors also play a big role in digital circuits, like logic gates and counters. In these, they do logical tasks, such as AND, OR, and NOT. This lets devices make choices and do math.
In summary, transistors are vital in electronic circuits. Their power to amplify or switch signals is key to many modern devices. Their role in transistor applications like amplifiers has changed our lives. As they evolve, we can expect even more advanced gadgets.
Amplification Properties of Transistors
Transistors are key in electronic devices because they can make weak signals stronger. This is why they’re used in many devices like audio amplifiers and radios.
Transistors have three main ways to amplify signals: current, voltage, and power. Current amplification boosts the current of a signal. Voltage amplification increases the voltage. Power amplification boosts the power of a signal.
Current Amplification
Current amplification is a big deal for transistors. It helps them make weak signals stronger. This is super useful in audio amplifiers, where a small input can become a big output.
Voltage Amplification
Voltage amplification is also important. It lets transistors increase the voltage of a signal. This is great for driving bigger loads, like speakers or motors.
Power Amplification
Power amplification is about making a signal’s power stronger. It’s really useful in things like radio transmitters. A small input can become a powerful output.

| Type of Amplification | Description |
|---|---|
| Current Amplification | Amplifies the current of a signal |
| Voltage Amplification | Amplifies the voltage of a signal |
| Power Amplification | Amplifies the power of a signal |
In short, transistors are vital in many electronic devices. They help make signals stronger. Knowing how they amplify signals helps designers make better circuits.
Temperature Effects and Thermal Considerations
Temperature is key for electronic devices. It can change how transistors work, leading to possible failures. For power transistors, it’s important to manage heat well.
In the world of semiconductors, keeping devices cool is vital. Thermal resistance is a measure of how well a device handles heat. It’s calculated by comparing temperature differences and heat flow. There are different ways to measure it, like using steady or short bursts of heat.
Several things can change a device’s thermal resistance. For example, how much current it carries and how much heat it makes. A study showed that a 35-W transistor’s thermal resistance changes with current at a fixed power of 20 W. This shows why we must think about how devices work when we design them.
To deal with temperature issues, we use methods like heat sinks and cool air. Knowing how temperature affects devices helps make them better and more reliable. Here are some key points for managing heat in electronics:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | The ratio of temperature difference to heat flow |
| Operating Conditions | Collector current, power dissipation, and ambient temperature |
| Thermal Management Techniques | Heat sinking, thermal interface materials, and forced air cooling |
By focusing on these areas and using the right cooling methods, we can make devices that work well in tough conditions. This is very important for power transistors, which are used in many areas, like cars and green energy systems.
Selecting the Right Transistor for Your Project
Choosing the right transistor for electronic projects is key. You need to look at gain, frequency response, and power handling. Knowing what your project needs will help you pick the best transistor.
For backlight control, a small signal NPN like the BC547 works well. But, for other tasks, you might need a different transistor. For example, the 2N3904 is great for driving relays in low-power setups.
Here are important things to think about when picking a transistor:
- Gain: How well the transistor can boost the input signal.
- Frequency response: The range of frequencies it can handle well.
- Power handling capability: The max power it can take without getting damaged.
By looking at these points and knowing what your project needs, you can choose the right transistor. This is important for your electronic projects.
| Transistor Type | Gain | Frequency Response | Power Handling Capability |
|---|---|---|---|
| BC547 | 100-200 | 100 MHz | 100 mA |
| 2N3904 | 50-100 | 100 MHz | 200 mA |
Common Troubleshooting Issues
Working with electronic devices can be tricky. Transistors often face issues like overheating, electrical noise, and failure. These transistor problems can be tough to deal with, but there are ways to fix them.
Many transistor problems come from simple mistakes. This includes wrong wiring or not enough cooling. To avoid these, always follow the right installation and care steps. Knowing common transistor problems helps you prevent failures.
Some common troubleshooting issues with transistors include:
- Overheating, which can damage the transistor and other parts
- Electrical noise, which can mess with the device’s work and cause errors
- Device failure, which means expensive fixes or a new device
Understanding and preventing these troubleshooting issues keeps your electronic devices working well. Whether you’re using NPN or PNP transistors, knowing the problems helps avoid costly repairs and downtime.
To help with troubleshooting issues, here’s a table with common problems and their fixes:
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Overheating | Improve cooling, reduce power use |
| Electrical noise | Use noise-cutting parts, shield sensitive spots |
| Device failure | Replace broken parts, check wiring and connections |
Safety Considerations When Working with Transistors
Working with transistors requires careful safety steps to avoid electrical shock and injury. Safety considerations are key when handling transistor handling to prevent accidents. Keeping electronic devices properly handled and stored reduces the risk of damage or injury.
To handle transistors safely, it’s important to follow the right steps. Wear protective gear like gloves and safety glasses. Also, keep your work area clean and organized to avoid accidents.
- Avoid electrical shock by ensuring proper insulation and grounding
- Prevent damage to electronic devices by careful handling and proper storage
- Follow proper procedures for transistor handling to reduce injury or damage risk
By following these safety considerations and taking precautions, you can have a safe and successful experience with transistors and other electronic devices.
Advanced Applications and Circuit Designs
Transistors are key in many advanced applications. They are found in high-frequency amplifiers, switching power supplies, and digital circuits. These circuit designs depend on transistors to boost or switch signals. This makes them essential in today’s electronic devices.
In these roles, transistors enhance efficiency, cut down power use, and boost performance. For instance, in high-frequency amplifiers, they amplify weak signals. This leads to clearer communication and quicker data transfer.
Some examples of advanced applications that use transistors include:
- Smartphones, which rely on transistors for efficient signal processing and battery life optimization
- Computers, which use transistors as digital switches in logic gates and microprocessors
- Power devices, which use transistors for effective energy control and voltage regulation
In conclusion, transistors are vital in advanced applications and circuit designs. They help make efficient, high-performance electronic devices. These devices are used across many industries.
Integration with Other Electronic Components
When designing electronic circuits, transistors often work with other parts like resistors, capacitors, diodes, and integrated circuits. This teamwork is key to making complex electronic devices. The right components depend on the task at hand. For example, resistors and capacitors manage current and voltage. Diodes and LEDs help with rectification and showing signals.
In circuit design, combining transistors with other components is vital. This mix allows for the creation of circuits that can do many things. It makes electronic circuits more efficient and effective.
Resistors and Capacitors
Resistors and capacitors are often paired with transistors. Resistors control current flow, while capacitors store energy. Together, they help make circuits like amplifiers, filters, and oscillators.
Diodes and LEDs
Diodes and LEDs also team up with transistors. Diodes convert current, and LEDs show signals. This team-up enables circuits to handle various tasks, from simple signals to complex processing.
Integrated Circuits
Integrated circuits combine many components, like transistors, resistors, and capacitors, into one package. This integration makes complex devices like microprocessors and memory chips possible.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Resistors | Control the flow of current |
| Capacitors | Store energy |
| Diodes | Rectification |
| LEDs | Indication |
| Integrated Circuits | Combine multiple components |
Transistors working with other components is key in electronic circuit design. By using transistors with resistors, capacitors, diodes, and integrated circuits, designers can make complex devices. This integration is essential for creating efficient circuits for many applications, from simple gadgets to complex systems.
Future Developments in Transistor Technology
Researchers are pushing the limits of transistor technology to make electronic devices better. They aim to create smaller, faster, and more efficient gadgets. New materials and ways to make them are key to these advancements.
These improvements will likely make our daily tech, like smartphones and computers, even better. For instance, transistor technology could lead to faster processors. This means our devices will work faster and be more reliable.
Experts are also looking into using transistor technology for quantum and neuromorphic computing. These areas could lead to big leaps in artificial intelligence and machine learning. The progress in transistor technology and electronic devices will drive these innovations.
The future of transistor technology looks bright for electronic devices. We can expect smaller, faster, and more efficient gadgets. These changes will change how we live and work.
Testing and Measurement Techniques
Working with electronic devices means you need the right tools for testing and measurement. Transistors, in particular, need special methods to check if they work right.
Using multimeters is a common way to test transistors. You connect the multimeter to the transistor’s terminals. This lets you measure the resistance and voltage drop. For example, a good PNP transistor should show a resistance of 500-1500 Ohms when you test the collector and emitter against the base.
Oscilloscopes are also useful for testing transistors. They help you see how the transistor acts in a circuit. This is great for checking if the transistor is switching correctly. By using these methods, you can make sure your devices work well and reliably.

Testing transistors often involves checking the forward voltage drop and looking for short circuits. You also need to check the current gain. By doing these tests and using the right tools, you can spot any problems with your transistors. This helps make sure your electronic devices work as they should.
Conclusion
Transistors have changed the world of electronics. They make devices smaller, faster, and more efficient. These tiny semiconductor devices are key to modern technology. They power everything from smartphones to medical equipment.
The progress in transistor technology is amazing. They can switch at speeds of hundreds of gigahertz and amplify current well. From common NPN and PNP transistors to special ones, they keep improving what’s possible in electronic devices.
Looking ahead, transistors will keep leading in tech innovation. They will help create even more powerful and flexible electronic systems. Their unmatched performance, reliability, and flexibility make them essential for the next big leaps in electronic devices.
FAQ
What are NPN and PNP transistors?
NPN and PNP transistors are key parts in electronic circuits. They help as amplifiers, switches, and logic gates. These semiconductor devices are used in many electronic applications.
How do NPN and PNP transistors differ in their structure and operation?
NPN transistors have a p-type material between two n-type materials. PNP transistors have an n-type material between two p-type materials. This difference affects how they control current and their uses in circuits.
What are the key applications of NPN and PNP transistors in electronic circuits?
Transistors are used in many ways, like amplifiers and switches. NPN transistors are good for fast switching or signal amplification. PNP transistors are better for low-noise or low-power circuits.
How do transistors function as switches in electronic circuits?
Transistors act as switches by controlling current flow. They operate in different modes to switch and amplify signals in various applications.
What are the common biasing techniques used in transistor circuits?
Circuits use biasing techniques like forward and reverse bias. These control charge carriers for amplification or switching. They’re key for transistor performance and efficiency.
How do temperature and thermal considerations affect the performance of transistors?
Temperature impacts transistor operation, affecting gain and leakage current. Proper cooling and protection circuits are vital for reliable transistor performance.
What factors should be considered when selecting the right transistor for a project?
Consider voltage and current ratings, power dissipation, and switching speed. Also, think about noise, packaging, and application requirements. This ensures the right transistor is chosen for the project.
What are some common troubleshooting issues with transistors, and how can they be resolved?
Issues like overheating and electrical noise can occur. These might be due to biasing problems or circuit design flaws. Thermal management and circuit analysis can help solve these problems.
What safety considerations should be taken when working with transistors?
Use anti-static equipment to prevent damage from electrostatic discharge. Also, consider temperature and humidity, and use protection circuits to safeguard transistors and systems.