A typical desktop computer system unit has about 4 to 7 main parts. These include the motherboard, CPU, RAM, hard drive, and input/output ports. Knowing these parts is key for anyone into computer hardware.
The CPU, motherboard, and RAM are vital. They work together to give a computer the power and storage it needs.
The motherboard is the main device that connects all parts. This includes video cards, RAM, sound cards, and hard drives. The CPU does billions of math calculations every second. RAM helps the CPU quickly share information but loses data when power is off.
Hard drives store data like music, videos, and documents. They can hold a lot of information, from 500GB to several terabytes.
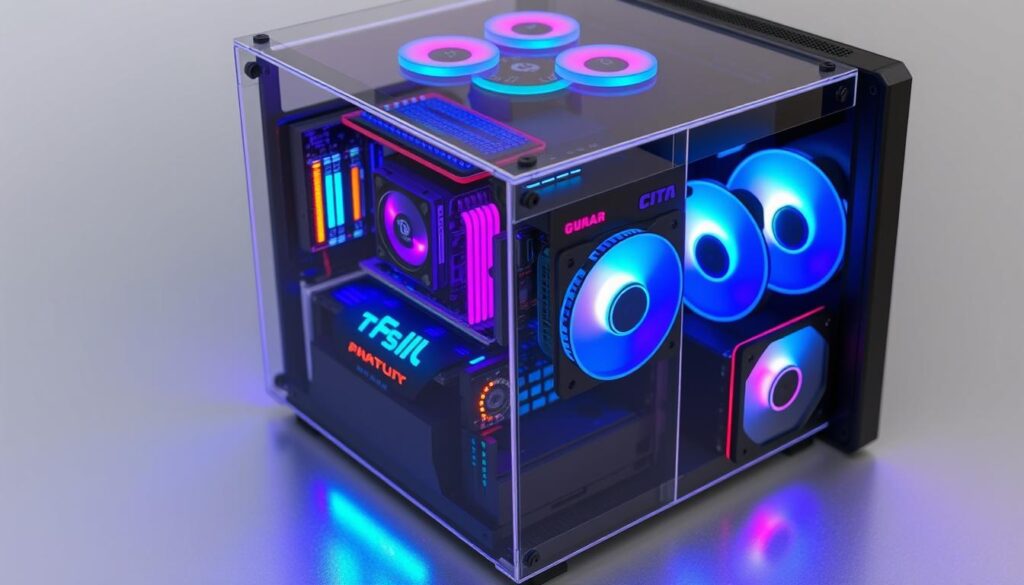

Computer hardware, like system unit parts, CPU, and motherboard, is key to a computer’s performance. RAM’s use greatly impacts speed. A system with 16GB RAM can handle many tasks at once.
A hard disk drive can store a lot of data, from 500GB to several terabytes. Most home computers have drives of 1TB or 2TB.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding system unit components is vital for computer hardware enthusiasts.
- The CPU, motherboard, and RAM are essential for processing and storage.
- Computer hardware, including system unit components, CPU, and motherboard, affects performance.
- RAM’s use greatly impacts speed, with 16GB RAM handling many tasks smoothly.
- A hard disk drive can hold between 500GB to several terabytes, with most systems having 1TB or 2TB drives.
- System unit components, including the motherboard, CPU, and RAM, are vital for a computer to function.
Understanding the System Unit Basics
The system unit is the heart of a computer. It holds key parts like the motherboard and CPU. Knowing the basics of the system unit is key. The CPU is vital for processing data, making the system work.
The CPU can do math and make logical choices. It has three main parts: the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), Control Unit (CU), and Memory Registers. These parts help the CPU carry out instructions and tasks.
What is a System Unit?
A system unit is where the computer’s main parts live. It includes the CPU, motherboard, and RAM. Knowing about the system unit helps us see how these parts work together.
Key Functions of the System Unit
The system unit does many important things. It processes data, stores it, and handles input and output. The CPU is the brain, executing instructions and tasks. It also has memory for handling many tasks at once.
Evolution of System Units
System units have gotten better over time. New technology has made CPUs stronger, storage bigger, and input/output faster. Knowing how system units have changed helps us understand today’s computers.

- The CPU is essential for data processing, and without it, the system unit cannot function.
- Graphics cards are integrated into approximately 70% of high-performance desktops as standalone components.
- RAM allows for the simultaneous handling of multiple tasks, with systems with 16GB of RAM able to run an average of 10 applications without significant slowdowns.
By learning about system unit basics and computer hardware, we can better understand how computers work.
The Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The central processing unit, or CPU, is often called the computer brain. It plays a key role in executing instructions and handling data. The CPU does calculations, executes instructions, and controls other computer parts.
In today’s computers, the CPU is a complex part. It has the control unit and arithmetic logic unit. These parts work together to process information and complete tasks. The CPU also has a cache memory, a small, fast memory for data it uses often.
The CPU’s instruction cycle includes fetch, decode, and execute steps. This cycle helps the CPU process instructions and tasks efficiently. Modern CPUs also have hyperthreading, making one core work like two, doubling its capacity.
Some key features of modern CPUs include:
- Cache memory sizes ranging from 1 MB to 32 MB
- Level 1 cache sizes ranging from 64 KB to 512 KB
- Hyperthreading capabilities
- Fast data retrieval speeds due to cache memory
In summary, the CPU is a vital part of the computer system. Its performance greatly affects the computer’s speed and efficiency. Knowing how the CPU works and its features helps us appreciate modern computers’ complexity and power.
Motherboard: The System’s Foundation
The motherboard is the main circuit board of a computer. It connects all hardware components together. It has important parts like CPU sockets, RAM slots, and power connectors.
The motherboard sends power from the Power Supply Unit (PSU) to the CPU and RAM. This is key for the system to work.
The motherboard is vital for computer hardware to work well together. It has data transfer interfaces like SATA and M.2 for fast SSDs. The BIOS or UEFI chip on the motherboard starts up the system and checks for function during startup.
Motherboard Form Factors
There are many motherboard form factors, like ATX, Micro ATX, and Mini ITX. Each has its own features and specs. The choice depends on the computer’s use, like gaming or server work.

Important Motherboard Components
Key components include the chipset, CPU socket, and RAM slots. The chipset handles data transfer. The CPU socket connects the CPU. RAM slots hold RAM modules.
| Motherboard Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Chipset | Manages data transfer between components |
| CPU Socket | Provides a connection point for the CPU |
| RAM Slots | Allow for the installation of RAM modules |
Choosing the Right Motherboard
Choosing the right motherboard depends on several factors. These include the computer’s use, CPU and RAM type, and budget. It’s important to look at the motherboard’s features, like USB and SATA ports, to meet your needs.
Random Access Memory (RAM)
RAM, or random access memory, is a key part of a computer. It stores data and apps temporarily while the CPU works on them. This makes it faster than hard drives or solid-state drives.
Laptops usually have 8 GB or 16 GB of RAM. For video editing, you need at least 16 GB. Adobe suggests at least 8 GB of RAM for Photoshop Creative Cloud on Macs.
There are two main types of RAM: DRAM and SRAM. DRAM needs constant power and is cheaper but slower. SRAM is faster but costs more.

Upgrading RAM can really boost your computer’s speed. DDR SDRAM, like DDR5, offers better speeds and uses less power. It’s important to pick the right RAM for your system.
| RAM Type | Capacity | Speed |
|---|---|---|
| DRAM | Up to 64 GB | Up to 3200 MHz |
| SRAM | Up to 16 GB | Up to 1600 MHz |
In summary, RAM is a critical part of your computer. Knowing about its types, capacity, and speed helps improve your computer’s performance.
Storage Devices and Options
There are many ways to store data, each with its own good and bad points. The main types are Hard Disk Drives (HDD), Solid State Drives (SSD), and NVMe.
Hard Disk Drives (HDD)
HDDs are the old-school choice, using disks and mechanical parts to read and write data. They’re cheap and hold a lot of data, making them a favorite for many.
Solid State Drives (SSD)
SSDs, by contrast, use flash memory for data storage. They’re faster and more reliable than HDDs but cost more.
NVMe Storage Solutions
NVMe SSDs are the fastest of all, using the NVMe protocol for super-fast data transfer. They’re perfect for tasks that need quick performance, like gaming and video editing.
Here’s a quick comparison of these storage devices:
- HDD: Big storage, low price, slow speeds
- SSD: Fast speeds, high price, medium storage
- NVMe: Super fast speeds, high price, medium storage

In summary, picking the right storage device depends on what you need. HDDs, SSDs, and NVMe each have their own benefits and drawbacks. Choosing wisely can greatly improve your system’s performance and your overall experience.
| Storage Device | Capacity | Transfer Speed | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDD | Up to 16TB | Up to 200MB/s | Low |
| SSD | Up to 8TB | Up to 7000MB/s | Medium |
| NVMe | Up to 8TB | Up to 10000MB/s | High |
Power Supply Unit (PSU)
The Power Supply Unit (PSU) is key in powering all parts of the system unit. A reliable PSU is vital for the computer’s smooth operation. It’s important to pick a PSU that meets or beats the system’s power needs.
A top PSU should have a high efficiency rating. It should be at least 80% efficient at 20%, 50%, and 100% loads, as 80 PLUS certification requires. Brands like CORSAIR offer PSUs with Cybenetics Gold efficiency and meet Intel’s ATX 3.1 power standard. These PSUs are reliable and efficient, great for demanding tasks.

- Wattage: The PSU’s wattage should be double the total wattage required by the components.
- Efficiency: Look for a PSU with a high efficiency rating, such as 80 PLUS Gold or Cybenetics Gold.
- Connectors: Ensure the PSU has the necessary connectors to support the system unit’s components.
In summary, a high-quality PSU is essential for a computer’s reliable operation. By looking at wattage, efficiency, and connectors, users can find a PSU that meets their needs. This ensures optimal computer power and efficient operation of the power supply unit. A well-chosen PSU also cuts energy use and reduces the risk of component failure, making it a critical part of any system unit.
Main Components of a System Unit
The system unit is the heart of a computer. It holds all the key parts that make it work. The main parts are the CPU, motherboard, RAM, and storage devices. These are vital for the system to run smoothly.
There are also secondary components like peripherals and expansion cards. These add to the system’s abilities. All these parts work together for a great computing experience. Knowing about them is key for setting up, improving, or fixing a computer.
Primary Components
Primary components are the core of the system unit. They include:
- CPU (Central Processing Unit)
- Motherboard
- RAM (Random Access Memory)
- Storage devices (Hard Disk Drives or Solid State Drives)
These parts are critical for the system to work right. Taking them out would harm the system’s performance.
Secondary Components
Secondary components add to the system’s abilities. They include:
- Peripherals (keyboard, mouse, monitor)
- Expansion cards (graphics cards, sound cards)
These parts can be added or taken away as needed. It depends on what the user wants.

In conclusion, knowing about system unit components is important. It helps users customize their systems to fit their needs. By understanding primary and secondary components, users can make better choices for their computers.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| CPU | Central Processing Unit, responsible for executing instructions |
| Motherboard | Main circuit board, connecting all components |
| RAM | Random Access Memory, providing temporary storage for data |
| Storage devices | Hard Disk Drives or Solid State Drives, providing permanent storage for data |
Cooling Systems and Heat Management
Cooling systems are key to stopping overheating and keeping system unit parts working long. Good heat management is vital for top performance and avoiding damage. Old systems like the IBM 3081 processor used Thermal Conduction Modules (TCMs) to cool chips. The Cray-1 supercomputer used a cooling system with refrigerant to keep chip temperatures at 69 °C (156 °F).
Nowadays, computer cooling systems use air or liquid cooling. Air cooling uses fans to move air and cool down. Liquid cooling uses water or a water-glycol mix to manage heat well. The Blue Gene supercomputer uses air cooling to save on costs and keep things simple.

Choosing the right cooling system is important. Look at energy use, noise, and how well it fits with your system. Some systems, like those using vapor-compression refrigeration, are very efficient. Others, like liquid cooling, might need more setup and upkeep.
Good cooling systems and heat management are essential for system unit reliability and performance. Knowing the value of cooling systems and picking the best one helps avoid overheating. It also cuts down energy use and makes your system last longer.
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
The Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is key in computer systems. It handles graphics and boosts visual performance. GPUs can be built-in or separate, each with its own benefits and drawbacks.
Integrated GPUs are common in laptops and light desktops. They manage basic graphics but can’t match the power of separate graphics cards.
Dedicated GPUs, by contrast, have their own memory (VRAM) and more power. They’re great for games and professional work. The architecture of GPUs makes them perfect for tasks needing lots of parallel work.

Some important GPU features are: * Fast memory bandwidth for quick data moves * Hundreds to thousands of processing units for parallel work * Support for 2D and 3D graphics, plus tasks like machine learning and video editing * Good at handling power and heat for better performance and reliability
In computer graphics, GPUs are essential for making images and videos. They’ve moved beyond just 2D and 3D to help with AI and video editing. As computing needs grow, GPUs will become even more vital for better visuals and faster calculations.
Input/Output Ports and Connectivity
Input/Output (I/O) ports are key for linking computer peripherals to the system unit. They make data transfer and communication smooth. Common ports include Universal Serial Bus (USB), High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI), and Ethernet.
These ports help devices talk to each other, making things run smoothly. For instance, USB 3.2 can move data at up to 20 gigabits per second (Gbps). Thunderbolt 3 can go even faster, up to 40 Gbps.
Some important features of I/O ports and connectivity include:
- USB hubs let you connect more devices to one USB port
- Adapters or cables help different I/O ports work together, like USB-C to USB-A
- Using encryption on I/O ports keeps data safe during transfer

In summary, I/O ports and connectivity are vital for a system unit. They make data transfer and communication between devices efficient. Knowing about different I/O ports and their features helps users improve their system’s performance and connectivity.
| I/O Port | Data Transfer Speed |
|---|---|
| USB 3.2 | Up to 20 Gbps |
| Thunderbolt 3 | Up to 40 Gbps |
Expansion Slots and Cards
Expansion slots are sockets on the motherboard for adding cards. These cards boost your computer’s performance. Most computers have different numbers of these slots, from 1 to 32 data lanes per PCIe port.
PCIe is the top choice for expansion slots today, replacing PCI and AGP. A motherboard can have 1 to 7 slots. Some systems can hold up to 19 cards. You can use these cards for graphics, sound, and networking.
Here are some common types of expansion slots:
- PCI slots, commonly used for sound and network cards
- PCIe slots, providing faster data transfer rates compared to PCI slots
- AGP slots, designed for high-performance graphics cards
- ISA slots, older and less used in modern systems due to slow data transfer rates
When picking expansion cards for upgrades, check your motherboard’s slots. The specs are in the motherboard manual. It tells you how many and what types of slots you have.

System Unit Form Factors
Building or upgrading a computer means thinking about the system unit form factors. The computer case is key, as it holds all the internal parts. Its size affects the system’s design and how well it works. Common sizes include tower cases, desktop cases, and all-in-one designs.
The tower case is a top pick for its flexibility and room for growth. It fits many system unit form factors, like ATX, Micro-ATX, and Mini-ITX. It also has plenty of space for cooling, power supplies, and more.
Desktop cases are smaller and perfect for tight spaces. They’re great for home offices or small work areas. All-in-one designs combine the system unit and monitor into one. They’re ideal for those who prefer a simple setup.
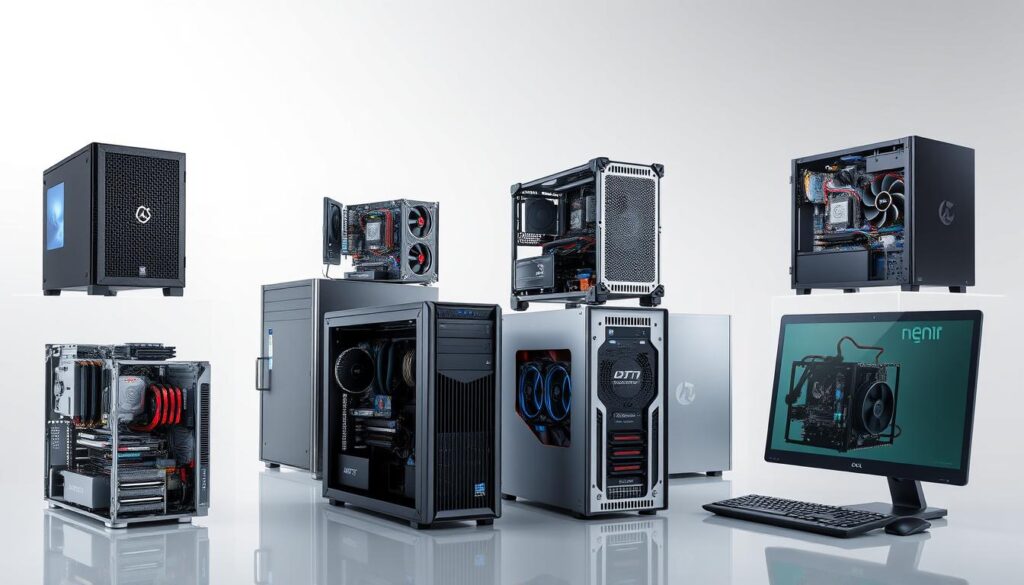

Choosing the right system unit form factor is key. Think about space, how easy it is to add new parts, and looks. The right choice makes upgrading and customizing easy. By picking the right system unit form factors and computer case, you get a system that’s both powerful and efficient.
| Form Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| ATX | Most common motherboard standard, used in approximately 50% of desktop systems |
| Micro-ATX | Smaller variant of ATX, used in approximately 35% of desktop systems |
| Mini-ITX | Designed for small form factor systems, used in approximately 15% of current computer builds |
Cable Management and Internal Organization
Keeping your system unit tidy is key. This means managing computer cables well. You should bundle them tightly and hide them behind the motherboard tray. This makes your system look neat and helps it cool better.
Use reusable ties like Velcro strips and twist ties to avoid damage. Start by securing cables from the top to the bottom of the case. This makes your system more organized. Modular power supplies, like the Corsair RM850e, also help by cutting down on cables.
There are many tools to help manage cables. You can use cable zip ties, under desk trays, and organizers. These tools keep your cables tidy and improve airflow. They also make your system look better.

Here are some benefits of proper cable management and internal organization:
- Improved cooling efficiency
- Enhanced airflow through the case
- Reduced risk of interference with airflow
- Improved appearance of the system unit
- Increased ease of maintenance and upgrades
By using the right tools and following these tips, you can make your system unit efficient and attractive. This will improve your computing experience.
| Cable Management Tool | Price | Description |
|---|---|---|
| NewMainOne 500-pack Cable Zip Ties | $14 | A pack of 500 cable zip ties for managing computer cables |
| Scandinavian Hub Under Desk Cable Management Tray | $25 | An under desk cable management tray for organizing cables and power strips |
| YaeCCC Cable Management Organizer | $20 | A cable management organizer for concealing cables and power strips |
System Unit Maintenance Tips
Regular system unit maintenance is key to making your computer last longer and avoid problems. Doing the right computer maintenance can save you from expensive fixes and keep your system running well.
To keep your system unit in top shape, do routine checks and maintenance. This means cleaning it, updating drivers, and watching the temperature. Troubleshooting common issues can also help you solve problems early on.
Here are some maintenance tips to remember:
- Clean the system unit regularly to prevent dust buildup
- Update drivers and software to ensure you have the latest security patches and features
- Monitor temperatures to prevent overheating
- Perform regular backups to safeguard your data
- Check for and install updates for your operating system and antivirus software
By following these tips, you can make your system unit last longer and avoid common problems. Always be gentle with your system unit. Avoid extreme temperatures or physical stress.

Future Trends in System Unit Design
The future of system unit design will be shaped by new technologies. These include modularity, sustainability, and better performance. As systems need to be more efficient and powerful, companies are working hard to innovate. Future trendswill see artificial intelligence, 5G, and IoT making systems smarter and more connected.
Emerging technologies like blockchain, AR, and VR will also shape the future. They will make systems more secure, immersive, and interactive. These systems will be used in gaming, education, and healthcare. The system unit design of tomorrow will need to be flexible and user-friendly.

Modular components will be key in the future of system unit design. They will let users upgrade and customize their systems easily. This will help reduce electronic waste and make systems more environmentally friendly.
Some benefits of these future trends include:
- Improved performance and efficiency
- Increased modularity and customization
- Enhanced security and connectivity
- Reduced environmental impact
Conclusion
Understanding the system unit is key for a computer’s performance. It includes the CPU, motherboard, storage devices, and cooling systems. Each part is important for a computer to work well.
Knowing about these components helps you make smart choices. This is true for setting up, fixing, and improving your computer. It’s all about making your computer better.
This guide is for anyone interested in computers. It’s for tech fans, IT students, or anyone wanting to improve their computer use. It gives you the tools to handle system units confidently.
With this knowledge, you can make your computer run better. You can also keep it safe and use it to its fullest. This is how you get the most out of your digital tools.
As technology changes, knowing how computers work becomes even more important. Keeping up with new tech helps you stay ahead. This ensures your computer stays useful and meets your needs.
Start learning about the system unit today. It opens up a world of digital possibilities. Get ready to explore and enjoy the latest in computer technology.
FAQ
What is the purpose of a system unit?
The system unit is the heart of a computer. It holds the CPU, motherboard, RAM, and storage devices. It processes information, runs software, and stores data.
What are the key components of a system unit?
Key parts include the CPU, motherboard, RAM, and storage devices like HDD, SSD, and NVMe. The power supply unit(PSU) and cooling systems are also important.
What is the role of the CPU in a system unit?
The CPU is the brain of the system unit. It handles information processing, executes instructions, and does calculations. The CPU’s performance greatly affects the computer’s speed.
How does the motherboard impact the system unit?
The motherboard is the base of the system unit. It connects and supports the CPU, RAM, and other components. Choosing the right motherboard is key for a good system unit.
What is the importance of RAM in a system unit?
RAM is vital for quick data access. It stores data and instructions for the CPU. More and faster RAM improves computer performance.
What are the different types of storage devices used in a system unit?
System units use HDD, SSD, and NVMe storage. Each type offers different benefits in speed, capacity, and reliability.
How does the power supply unit (PSU) affect the system unit?
The PSU powers the system unit’s components. Choosing the right PSU is critical for stable and efficient system operation.
What are the primary, secondary, and optional components of a system unit?
Primary components are essential for basic functions like the CPU, motherboard, RAM, and storage. Secondary components include peripherals like graphics and sound cards. Optional components add extra features like cooling systems.
Why is proper cooling important for a system unit?
Cooling keeps components at the right temperature. Without it, overheating can damage the system and reduce performance.
What is the role of the graphics processing unit (GPU) in a system unit?
The GPU handles graphics tasks like gaming and video editing. A dedicated GPU boosts visual performance and capabilities.
What are the common input/output (I/O) ports found in a system unit?
System units have ports like USB, HDMI, and Ethernet. These ports connect peripherals and expand the system’s capabilities.
How do expansion slots and cards affect the system unit?
Expansion slots let you add cards for graphics, sound, and networking. These cards enhance the system’s capabilities and support upgrades.
What are the different form factors of system units?
System units vary in form factors like desktops, towers, and all-in-ones. The choice depends on space, expandability, and looks.
Why is cable management and internal organization important for a system unit?
Good cable management improves airflow and reduces dust. It keeps the system cool, efficient, and easy to upgrade.
What are some tips for maintaining and troubleshooting a system unit?
Regular maintenance like cleaning and driver updates is key. Troubleshooting involves checking connections and updating drivers to fix issues.